Minerals play a crucial role in the sustenance of life as well as industrial applications. Among these, calcite is one of the most versatile minerals with a wide range of uses across various industries. Calcite, a carbonate mineral, is the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate. It is a common constituent of sedimentary rocks, limestone in particular, much of which is formed from the shells of dead marine organisms.
One of the primary uses of calcite is in the production of lime and cement. These are critical components in the construction industry, thus making calcite a vital resource in the global economy. Additionally, finely ground calcite, due to its high brightness and light scattering characteristics, is used as a filler in a variety of products ranging from plastics, paints, and paper to pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Moreover, due to its transparent nature, high-quality calcite is also used in the production of optical instruments. Hence, calcite’s importance cannot be understated.
Importance of Calcite in Different Industries and Applications
As the backbone of the limestone industry, calcite indeed plays a dynamic role in numerous sectors. In the realm of construction, it’s utilized as a structural component in the production of cement and lime. It’s also found in asphalt and concrete, which are critical in road construction and building projects.
But that’s not all. In the agriculture industry, calcite is used as a soil conditioner. It adjusts the acidity of the soil and provides essential minerals for plant growth.
Think that’s impressive? Well, there’s more. Calcite also finds its application in the realm of optics. High-grade optical calcite was used in World War II for gun sights, specifically in bomb sights and anti-aircraft weaponry.
In the pharmaceutical industry, calcite serves as a source of calcium, which is utilized in antacids and dietary calcium supplements.
Moreover, it has a role in water treatment. It’s used to neutralize acidic water and remove impurities.
Clearly, the importance of calcite extends beyond mere geological curiosity. It’s a versatile mineral that plays a pivotal role in diverse industries, from construction to medicine, agriculture, and optics.
Construction Uses of Calcite

The construction industry heavily relies on calcite, particularly cement and concrete production. Its unique properties contribute to the strength and durability of these materials. Calcite also serves as an essential filler in mortar, enhancing its workability and binding capacity. Furthermore, this mineral plays a significant role in the production of lime, a critical component in many construction processes. Each of these uses underlines the indispensability of calcite in construction.
Used in Cement and Concrete Production
Transitioning from an overview of calcite’s significance across industries, attention is now drawn to its integral role in construction, specifically in cement and concrete production. The use of calcite, primarily in the form of limestone, is pivotal in producing Portland cement, the most common type of cement used around the world. It contributes significantly to the bonding properties, durability, and resilience of the finished product.
Research indicates that approximately 5% of global carbon dioxide emissions stem from cement production, underlining the industry’s environmental impact. However, integrating calcite into cement production can reduce these emissions by up to 30%. This is achieved by replacing a portion of traditional cement materials with calcite, thus lowering the energy-intensive process of heating materials.
This innovative use of calcite not only enhances the quality of cement and concrete but also contributes to sustainable construction practices, demonstrating its multifaceted value in this sector.
Used as Filler in Mortar
Building on the significance of calcite in various industries, it is essential to delve deeper into its specific application in the construction industry. Particularly, the role of calcite as a filler in mortar warrants attention.
Calcite, due to its crystal nature, exhibits excellent binding properties which make it an ideal filler material in mortar. As a result, it significantly enhances the durability and overall performance of the mortar, rendering it more efficient for construction purposes.
A report by the International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology highlights that mortars containing calcite filler exhibit excellent workability, better cohesion, and improved water retention, which are critical for the longevity of structures. The incorporation of calcite into mortar also allows for the production of a more consistent product, reducing variations often associated with natural materials.
Furthermore, calcite’s white color contributes to the aesthetic appeal of mortar, which is a valued attribute in the construction of high-end residential and commercial buildings.
Used in the Production of Lime
Having traversed the broad applications of calcite in diverse industries, it becomes imperative to delve into its specific uses in the construction field. One such significant role is its utilization in the production of lime.
Lime, scientifically known as calcium oxide, is an essential substance in the construction industry. It is a product of calcite decomposition. When calcite is subjected to high temperatures, it decomposes to produce lime and carbon dioxide. This process is known as calcination. The importance of lime in construction cannot be overstated. It serves as a binding agent in construction materials such as mortar and concrete.
In addition, lime is used for soil stabilization in road construction. It reacts with clay minerals in the soil, enhancing the soil’s physical properties and reducing its susceptibility to damage by rain or traffic. Lime production from calcite thus plays a critical role in the construction industry, reinforcing the significance of this versatile mineral.
Agricultural Uses of Calcite
The agricultural utility of calcite is multifaceted. Primarily, it’s utilized in fertilizer production, contributing essential nutrients to soil health. Additionally, as a liming agent, it neutralizes acidic soils and fosters optimal growing conditions. Moreover, calcite’s role as a soil conditioner and pH regulator furthers its agricultural significance, improving soil texture and maintaining the crucial balance of soil acidity and alkalinity. Each of these applications underscores the essential role of calcite in agriculture.
Used in the Production of Fertilizers
Transitioning from the hard-hat zones of construction, the use of calcite takes a surprising turn towards the verdant fields of agriculture. In this sector, calcite plays an essential role in the production of fertilizers.
The unique chemical characteristics of calcite make it an invaluable ingredient in manufacturing fertilizers. As a source of calcium, calcite is often used in the production of calcium-based fertilizers. Calcium is a crucial nutrient for plant growth, promoting cell wall strength and assisting in nutrient uptake.
Notably, the application of calcite-based fertilizers has been linked to increased crop yields. According to the International Journal of Agronomy, a study revealed that using calcium-rich fertilizers can boost wheat yield by up to 20%.
However, the benefits are not just limited to yield increases. Fertilizers containing calcite can also improve soil structure, fostering the growth of beneficial soil microbes and enhancing nutrient availability.
Liming Agent
Looking beyond construction, the utility of calcite extends to the agricultural field as well. Specifically, the role of calcite as a liming agent shines brightly.
In the realm of agriculture, soil acidity can greatly affect the growth and yield of crops. Research has shown that excessively acidic soils can hinder the absorption of essential nutrients by plants. In the form of ground limestone, Calcite is used extensively as a liming agent to neutralize these acidic soils.
The use of calcite as a liming agent has a dual purpose. On the one hand, it increases the pH of acidic soils, making them more conducive for plant growth. On the other, it supplies a substantial amount of calcium, an essential nutrient for plant growth, to the soil.
Thus, the use of calcite as a liming agent not only enhances the fertility of the soil but also contributes to higher crop yields, making it an invaluable resource in agriculture.
Used as a Soil Conditioner and Ph Regulator in Agriculture

Transitioning from the towering edifices of construction to the expansive, verdant fields of agriculture, calcite demonstrates its versatility yet again. In agricultural settings, calcite serves as a key soil conditioner and pH regulator. Soil pH, a measure of its acidity or alkalinity, has a significant influence on plant health and productivity. Calcite, being alkaline, is used to neutralize acidic soils, thereby making it more conducive for plant growth.
The application of calcite aids in creating a healthier soil environment by enhancing water penetration and improving the soil’s structure. It also plays a significant role in the availability of essential nutrients. For instance, if the soil pH is too acidic, nutrients such as phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen become less accessible to plants. By using calcite to regulate soil pH, these vital nutrients are made more accessible, promoting healthier plant growth and higher crop yield. Thus, calcite emerges as an indispensable ally for farmers and agriculturalists in maintaining soil health and enhancing crop productivity.
Industrial Uses of Calcite
Calcite, primarily sourced as calcium carbonate, has varied industrial applications. One key use is in the paper and pulp industry, where it enhances paper brightness and smoothness. Another substantial application is in water treatment processes, where it functions as a neutralizer for acidity and a remover of impurities. Furthermore, the production of paints, coatings, and pigments also heavily utilizes calcite, underpinning its significance in these industries.
Source of Calcium Carbonate
Branching out from its agricultural applications, calcite’s significant role in various industrial processes merits attention. Consider the production of calcium carbonate, a key ingredient in numerous industries.
Calcite is a prime source of calcium carbonate, a mineral compound commonly used in the manufacturing sector. Extracted from the earth’s crust, calcite deposits are processed to obtain pure calcium carbonate. This industrially important compound features in several sectors due to its versatility and abundance.
Calcium carbonate obtained from calcite is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option compared to synthetic sources. The extraction and processing of calcite have minimal environmental impact, making it a sustainable choice for industries. Additionally, the wide distribution of calcite worldwide ensures a steady supply of calcium carbonate.
Calcium carbonate, derived from calcite, is a critical component in various industries, demonstrating the industrial importance of this common mineral. This underlines calcite’s significant contribution beyond the agricultural realm, highlighting its industrial potential.
Use of Calcite in the Paper and Pulp Industry for Paper Brightness and Smoothness
Transitioning from agricultural applications, calcite also extends its functionality to the paper and pulp industry. In this sphere, calcite, primarily in the form of ground limestone, serves a dual purpose: enhancing paper brightness and contributing to its smoothness.
The brightness of paper is a critical factor in its appearance, affecting its perceived quality and readability. Ground limestone, rich in calcite, is employed as a filler during the paper production process, which results in a significant improvement in the paper’s brightness. A study by the International Journal of Advanced Engineering Research and Studies revealed that the addition of calcite increased the brightness of paper by 5-10%.
Furthermore, the smoothness of paper, which is essential for printability and a comfortable reading experience, is also influenced by calcite. The small, regular particles of ground limestone fill the spaces between the paper fibers, creating a smoother and more uniform surface. Thus, the use of calcite in the paper and pulp industry is crucial for enhancing both the aesthetic and functional qualities of paper.
Use of Calcite in Water Treatment Processes to Neutralize Acidity and Remove Impurities
Shifting gears from the agricultural realm, the value of calcite extends to water treatment processes. Calcite, primarily composed of calcium carbonate, serves as an effective means to neutralize acidity and remove impurities in water systems. It performs this critical role by reacting with acidic water to increase the pH levels, thereby reducing the corrosivity and leaching of potentially harmful metals.
Given the need for safe, potable water across the globe, one cannot underestimate the importance of this application. Calcite’s role in enhancing water quality is, therefore, paramount. Its use in water treatment systems not only ensures the safety and palatability of drinking water but also extends the longevity of pipes and equipment by reducing corrosion.
Furthermore, calcite’s ability to remove impurities makes it a vital component in numerous industrial water treatment processes. This widespread application further underscores calcite’s industrial importance, marking its versatility and indispensability in various sectors.
The Manufacturing of Paints, Coatings, and Pigments
Moving away from the agricultural realm, let’s set our sights on the vast industrial applications of calcite. One of the most prominent uses is in the manufacturing of paints, coatings, and pigments.
Calcite plays an indispensable role in this industry. The mineral, in its grounded form, is a crucial component of latex paint, acting as an extender to increase the product’s volume. This addition not only makes the paint cost-effective but also enhances its properties. The application of calcite increases the paint’s hiding power, ensuring that the coat covers the surface uniformly and completely.
Furthermore, calcite provides increased weather resistance to the paint, making it perfect for outdoor applications. Its unique properties give the coating a smooth finish and the desired gloss, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the painted surface.
In the pigment industry, calcite is preferred for its high brightness and whiteness, which contribute to producing vibrant and true colors.
Decorative Uses of Calcite
The decorative uses of calcite can be appreciated in three key areas. Firstly, the creation of decorative stones and countertops highlights the aesthetic versatility of calcite. Secondly, the production of high-quality marble and limestone is a testament to calcite’s essential role in the production of these highly sought-after materials. Lastly, the importance of calcite in the fields of architecture and interior design underscores its functionality beyond aesthetics, including its durability and ease of manipulation.
Creation of Decorative Stones and Countertops
Moving beyond the industrial realm, consider another significant use of calcite – the creation of decorative stones and countertops. Known for its versatility and aesthetic appeal, calcite is a favored material in the decorative stone industry. It is often shaped into various forms such as countertops, tiles, and ornamental stones, adding elegance and sophistication to homes and commercial establishments alike.
The use of calcite in producing high-end countertops is particularly noteworthy. This mineral’s inherent translucency allows for a unique depth of color, resulting in a wide array of stunning surfaces. Furthermore, its ability to accept a high polish elevates the quality and visual appeal of the finished product.
Moreover, calcite’s hardness, which measures 3 on the Mohs scale, while less than that of quartz or granite, is still suitable for less-trafficked areas. This makes it an ideal choice for bathroom vanities, wall coverings, and other decorative applications. The use of calcite in decorative stone creation, therefore, contributes significantly to the beauty and functionality of architectural spaces.
Production of High-Quality Marble and Limestone
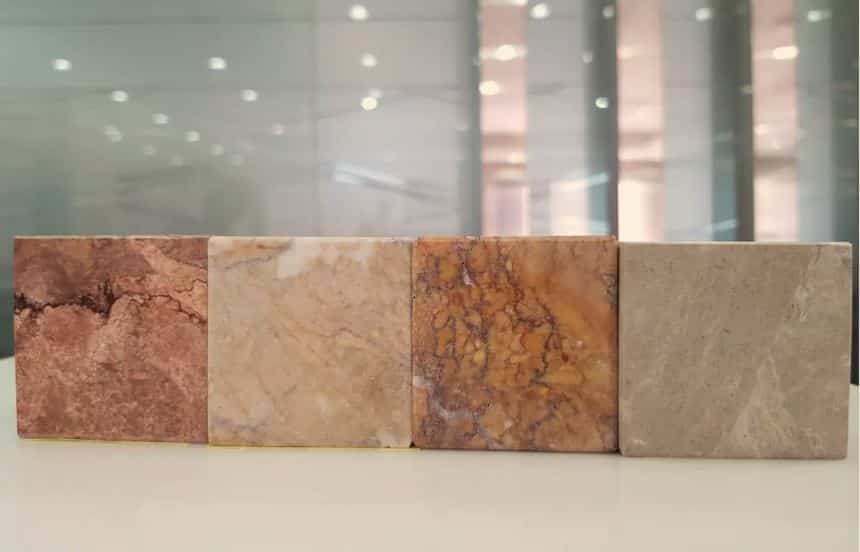

Beyond the realm of industry, calcite finds ubiquitous use in the decor sector. Attention must be drawn to the role calcite plays in the production of high-quality marble and limestone– two prime materials cherished in the construction business. Calcite, an indispensable origin of both materials, accounts for their unparalleled strength, lustrous sheen, and durability.
What’s more, it’s worth noting that marble and limestone, thanks to their calcite content, possess a natural aesthetic appeal. This makes these materials an ideal choice for premium countertops, grandiose statues, and exceptional architectural elements. Moreover, the crystal clear, white color of calcite makes these materials highly desirable for the construction of luxury homes, hotels, and commercial buildings.
In essence, the significance of calcite extends far beyond industrial applications, firmly rooting itself in the production of top-tier marble and limestone. This, in turn, has profound implications for architecture and interior design, further solidifying calcite’s indispensable role across diverse sectors.
Importance of Calcite in the Field of Architecture and Interior Design
Bridging from industrial to aesthetic applications, calcite has also found substantial utility in the realm of architecture and interior design. Its natural beauty and versatility lend a unique, timeless elegance to buildings and spaces alike.
In architecture, the use of calcite is not merely confined to the realm of aesthetics. Notably, it is also valued for its practical benefits. Calcite-based materials, such as limestone and marble, possess excellent durability and resistance to weathering, making them ideal for use in building facades. Additionally, these materials offer a broad spectrum of colors and textures, providing architects with a considerable palette to work with.
Within the world of interior design, calcite is often employed in crafting decorative elements such as fireplaces and statues, as well as high-end countertops and flooring. Its light-reflecting properties enhance the illumination within a room, thereby creating a feeling of spaciousness and grandeur.
In essence, the importance of calcite to architecture and interior design is underscored by its marriage of practicality with aesthetic appeal.
Optical and Electronic Applications
Calcite’s use in optical instrument and lens manufacturing is crucial due to its unique refractive properties. Its application in polarizing filters and glare reduction leverages its birefringence and double refraction features, enhancing visual clarity. Additionally, in the electronics sector, calcite’s role in producing components and optical devices cannot be understated. It’s often used in liquid crystal displays and other high-precision electronic devices, further emphasizing its versatility and importance.
Utilization of Calcite in the Manufacturing of Optical Instruments and Lenses
Moving beyond aesthetic applications, calcite plays a crucial role in the realm of optics and electronics. Consider the manufacturing of optical instruments and lenses; it’s here the invaluable properties of calcite come to the fore.
As a double-refracting mineral, calcite effectively splits light into two rays, a property known as birefringence. This unique characteristic makes it highly suitable for the production of polarizing prisms used in optical instruments such as microscopes, telescopes, and cameras.
When carefully cut and polished, calcite crystals can be used to create high-precision lenses. These lenses, owing to calcite’s exceptional light dispersing properties, provide superior quality images, making them indispensable in high-end optical research and photography equipment.
In essence, the utilization of calcite in optical instruments and lens manufacturing greatly enhances the functionalities of these devices, ultimately contributing to advances in scientific research and technology.
Importance of Calcite in Polarizing Filters and Glare Reduction Applications

Moving beyond the realm of decor, calcite demonstrates impressive capabilities in the field of optical technology. Specifically, its remarkable ability to polarize light finds extensive applications in glare reduction and the creation of polarizing filters.
Calcite, in its purest form, has a light transmission efficiency of almost 90%. This makes it an ideal material for the manufacturing of polarizing filters, which are indispensable for reducing glare in optical devices such as cameras and binoculars. The property of double refraction exhibited by calcite results in splitting light into two rays, one of which is absorbed by the filter, thereby reducing glare.
The use of calcite in glare reduction technology is not just limited to optical devices. For example, in aviation, the polarized windows of aircraft often incorporate calcite to reduce glare and enhance the pilot’s visibility.
Thus, calcite’s role in polarizing filters and glare reduction applications is pivotal, contributing significantly to the advancement of optical technology.
Use of Calcite in the Production of Electronic Components and Optical Devices
Moving beyond its aesthetic appeal, calcite plays a crucial role in the technological world, particularly in the realm of electronic components and optical devices. Calcite finds extensive use in the manufacturing of a diverse range of electronic products, owing to its unique electrical properties, such as low dielectric constant and resistivity.
It is integral to producing piezoelectric devices, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, and vice versa. The unique crystal structure and electro-mechanical properties of calcite make it an ideal material for such applications.
Furthermore, calcite is key to the production of optical fibers, a vital component in telecommunications and broadband networks. The high refractive index and birefringence of calcite contribute to enhancing the transmission of light signals in these fibers, thereby improving data speed and reliability.
In summary, the critical role of calcite in the electronics and optics industry should not be underestimated. Its unique properties contribute significantly to the efficiency and functionality of a plethora of devices.
Biological and Medical Applications
Calcite’s significant role in the formation of various biological structures such as shells, coral reefs, and skeletal systems is the first area of discussion. The discourse then transitions to the prevalent use of calcite in dietary supplements and calcium-rich medications, elucidating the mineral’s importance in sustaining human health. Finally, potential applications of calcite in the burgeoning fields of biomedical research and regenerative medicine will be explored, underscoring the mineral’s promising future in medical advancements.
Exploring Calcite’s Role in the Formation of Shells, Coral Reefs, and Skeletal Structures
Moving beyond the realm of optics and electronics, calcite also plays a pivotal role in the biological world, especially in the formation of shells, coral reefs, and skeletal structures. The crystalline structure of calcite imparts strength and durability to these biological structures, aiding in their longevity.
In the marine world, mollusks such as oysters and clams rely on calcite for the construction of their shells. This mineral is also an essential component in the formation of coral reefs, which are vital ecosystems supporting a vast array of marine life. The Emperor scorpion, a species known for its exoskeleton’s hardness, also employs calcite to reinforce its skeletal structure.
Moreover, many avian species rely on calcite to fortify their eggshells. The mineral’s perfect cleavage and rhombohedral crystal habit contribute to the shells’ robustness, providing essential protection for the developing embryo within. Thus, calcite’s role in the biological world is as fascinating as its applications in the realms of optics and electronics.
Use of Calcite in Dietary Supplements and Calcium-Rich Medications
Moving from its electronic applications, calcite also commands considerable significance in the fields of biology and medicine. Predominantly, it is instrumental in the manufacturing of dietary supplements and calcium-rich medications. Owing to its high calcium content and bio-compatible nature, calcite finds its application in the formulation of calcium supplements. In fact, a high percentage of over-the-counter calcium supplements are derived from calcite. This mineral is preferred for its cost-effectiveness, availability, and high calcium concentration. In addition, it also provides an efficient way to treat and prevent conditions related to calcium deficiency such as osteoporosis. To add to it, calcite-based supplements have been found to exhibit good absorption and bioavailability properties, making them a preferred choice for supplement formulation. These attributes place calcite at the heart of the pharmaceutical industry, especially in the development of calcium-rich medications.
Potential Applications of Calcite in Biomedical Research and Regenerative Medicine
On a similar note, the potential applications of calcite in biomedical research and regenerative medicine start to come into focus. The unique properties of calcite, particularly its biocompatibility and bioactivity, have sparked interest among researchers. Studies have demonstrated the potential of calcite to facilitate bone and tissue regeneration. For instance, calcite-based materials have been successfully used in bone grafting procedures as a substitute for natural bone.
Moreover, calcite’s ability to deliver a controlled release of drugs makes it a promising material in the design of drug delivery systems. Specifically, researchers have experimented with calcite nanoparticles as a vehicle for the delivery of therapeutic agents in cancer treatment.
In summary, these findings highlight the potential of calcite not only as a key player in the formation of shells, coral reefs, and skeletal structures but also as a valuable resource in the field of biomedical research and regenerative medicine.
In summation, the versatility of calcite is showcased across a range of industries including construction, agriculture, and industrial processes. Its unique characteristics make it a valuable resource in the creation of building materials, soil treatment, and various manufacturing processes.
Additionally, the use of calcite in decorative purposes, and optical, electronic, biological, and medical applications further emphasizes its significance. Whether it is appreciated for its aesthetic appeal, or utilized for its optical properties and biomedical potentials, calcite undoubtedly plays a pivotal role in various sectors.




